Describe the Types of Immunity and Give Examples of Each
Immunity may be passive or active. The word immunity is derived from a latin word Immunitas which means freedom from disease.
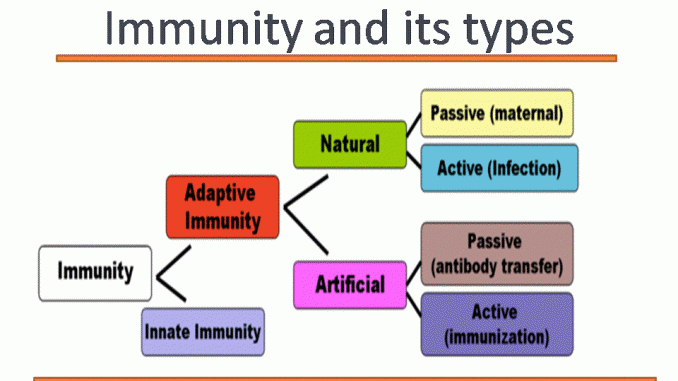
Immunity And Its Types Innate And Acquired Immunity Online Biology Notes
Generated in response to normal infection or in response to vaccine antigens.

. This is known as innate immunity. Severe combined immunodeficiency SCID. Nonspecific Resistance Innate Immunity 3.
Immunity derived from antibodies from another body such as given through mothers milk or. Types of Acquired Immunity Active Immunity. Examples of active immunity are numberless because your body is exposed to and reacts to new pathogens every day Passive Immunity.
In this case immunity is longer lived although duration depends on the. Passive immunity occurs when we are protected from a pathogen by immunity gained from someone else. For example measles antibody will protect a person who is exposed to measles disease but will have no effect if he or she is exposed to mumps.
This information replicates in every new generation of these cells and thus generates an even more effective defense system against each wave of infection. The immune system is made up of two parts. What is an antigen.
How do vaccines work to protect us from specific pathogens. Another example would be the exposure to a disease such as the chicken pox or a cold virus the patient produces. What is a self-antigen.
Active immunity and passive immunity are two types of adaptive. The first line of defence in a human body against pathogens is through barriers such as the skin mucus layers and saliva. The innate general immune system and the adaptive specialized immune system.
In adaptive immunity activated T and B cells whose surface binding sites are specific to the. Give the layers of the dermis and describe each. List 3 different forms of antigen that may be used for artificially acquired active immunity and state 2 common examples of each.
The third line of defence is through adaptive immunity. Physical and Chemical Barriers Innate Immunity 2. An example of active immunity would be vaccinations after receiving a vaccination the patient produces antibodies in response to a foreign antigen but the pathogen is dead or weakened.
Any contributions not made by. Describe the difference between active and passive immunity. In active immunity there are two types of immunity.
Immunity derived from antibodies generated by own body. Here are some common examples. Natural or Innate immunity.
The second line of defence is through phagocytes. It develops in response to an infection or vaccination. In active immunity the patient produces antibodies which are life long.
It creates antibodies in the natural world in response to harmful infections like measles. The Immune System has 3 Lines of Defense Against Foreign Pathogens. Involves the introduction of external antibodies.
Chapter 16 Innate Immunity list the cells of innate immunity and the basic role of each describe the mechanism of phagocytosis describe or. Active immunity involves the direct response to a foreign antigen within the body. Solution for Describe types of innate immunity.
The immune system fights germs and foreign substances on the skin in the tissues of the body and in bodily fluids such as blood. Stomach and blood vessels for example. When you are immune to a disease your immune system can fight off infection from it.
Give examples of each. In our blood there are white blood corpuscles. What is the difference between a naturally acquired and artificially acquired immunity.
An Individuals own immune system produces the antibodies needed. These two systems work closely together and take on different tasks. Active Immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease.
Response takes time to develop and there is a lag phase. Active immunity is the most common type. There are two types of immunity.
Children are in constant danger of infections from bacteria viruses and fungi. The adaptive immune system works because the immune cells responsible for it are each able to recognize and respond to one specific antigen or a few very similar ones. Direct contact with antigen stimulates antibody production.
In this article we compare and contrast two types. Immunity is defined as the bodys ability to protect itself from an infectious disease. Furthermore antibodies are produced artificially when they are produced in response to controlled exposure to an attenuated pathogen which is vaccination.
Each type of lymphocyte has a receptor for each antigen presented by the pathogen. This is again produced by innate immunity. These methods expose your immune system to a type of germ or pathogen in vaccinations just a.
The pathogen does not need to have direct contact with the body. This is an example of an immune deficiency that is present at birth. Artificially acquired passive immunity.
The adaptive immune responses depends on the function of two types of lymphocytes called B cells and T cells. What different types of vaccines are there. In the case of the acquired or adaptive immune system the body remembers the pathogens it has encountered in the past.
Both of these different types of immunity can be acquired in different ways. During passive immunity antibodies made in another person or animal enter the body and the immunity is short-lived and Active Immunity. Artificially acquired active immunity.
This is a direct result of the active immune system. Two types of immunity exist active and passive. It is an in-born immunity.
Active immunity can be acquired. Give 2 examples of enzymes that contribute to bacterial virulence and indicate their function. Define and give at least one example of each of the following types of immunity.
The innate immune system has a number of first line barriers to infection that are in place to prevent the entry and growth of pathogensThis article shall consider the physical physiological chemical and biological barriers that perform this role as well as clinical conditions that may result from their failure. Specific Resistance Acquired Immunity Physical and Chemical Barriers Innate Immunity Physical and chemical barriers form the first line of defense when the body is invaded. Examples of Active Immunity.
Symptoms of a weakened immune system. This disorder is sometimes called bubble boy disease. Active immunity occurs when our own immune system is responsible for protecting us from a pathogen.
In the case of active immunity antigens enter the body and the body responds by making its own antibodies and B-memory cells. There are two main types of immunity. Natural immunity is inheritedtransmitted from parents to offspring.

Active Vs Passive Immunity Differences And Definition Technology Networks

Acquired Immunity What Is It And How Do You Get It

Different Types Of Acquired Immunity Nursing School Notes Nursing School Survival Immunity Nursing
Comments
Post a Comment